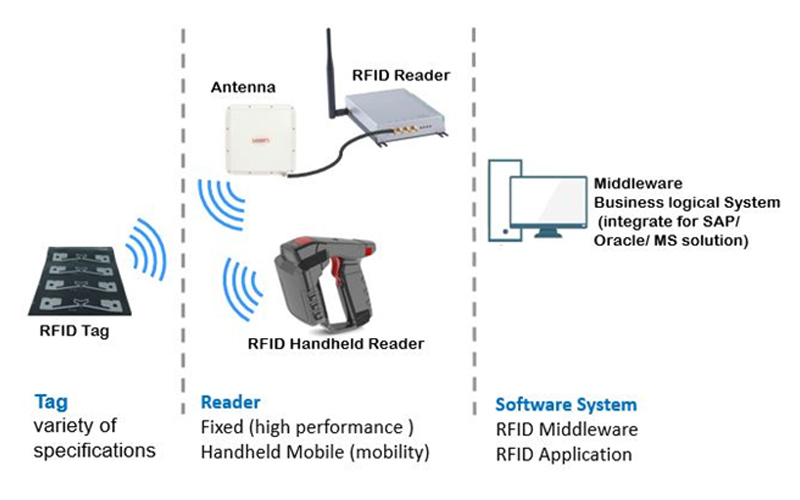
RFID software is used to process data sent to and received from radio frequency identification (RFID) devices such as RFID readers, writers, and printers. There are many different types of RFID software. Some RFID applications are used to produce RFID tags, tiny transponders that attach to RFID antennas. Others are designed to print RFID labels that include human-readable text or barcodes. RFID software for handheld devices such as readers, encoders, and scanners can reside on a network server or be embedded in the device. Traditional RFID middleware includes device management features such as remote monitoring and hardware configuration. Newer products such as RFID middleware appliance are hardware-software hybrids. Many RFID software applications provide system integration, and are designed for use with supply chain management (SCM), entERPrise resource planning (ERP), or warehouse management systems.
RFID software enables warehouses to produce RFID tags and RFID labels that meet electronic product code (EPC) and U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) standards. Product information such the stock keeping unit (SKU) and universal product code (UPC) are used to produce EPC complaint global trade identification numbers (GTIN), 14-digit data structures that identify products at a consumer-unit level. Some RFID software can also generate EPC compliant serialized global trade identification numbers (SGTIN) and serialized shipping container codes (SSCC).
Companies that do business with the United States government should select RFID software that can produce DoD96 RFID tags and MIL-STD-129P RFID labels. Typically, these RFID applications retain data for the electronic submission of advanced shipment notices (ASN) to the DoD’s wide area workflow (WAWF) system. RFID systems that can send data to internal ERP, accounting, and inventory management systems are also available. RFID software is designed to run on operating systems such as Windows® Server 2003, Solaris® 9 or 10, and Red Hat EntERPrise Linux®. Windows Server 2003 is an operating system (OS) from Microsoft that is designed for small devices such as handheld computers and personal digital assistants (PDA). The graphical user interface (GUI) is similar to versions of Windows used with personal computers (PC). Solaris® is a UNIX®-based operating environment that includes the SunOS® operating system, a graphical user interface (GUI), and open networking computing (ONC). Red Hat® EntERPrise Linux® is a leading open-source platform Red Hat, Inc. Windows and Microsoft are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Solaris and SunOS are registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. Red Hat is a registered trademark of Red Hat, Inc.